Systems Programming (XMUT): Assignment 3
“Database Management System”
- Due 17 November, 7 pm (Xiamen Time)
Resources and links:
To Submit
Do not rename these files.
This part will test whether you can apply the conceptual knowledge you have learned to solve practical programming tasks. You may only use the Standard C Library to perform the tasks in this part.
You will implement a simple database management system (DBMS). DBMS is a systems program that performs storage, retrieval, and updating of data in a computer system. DBMS addresses two major problems in conventional file-based systems: data redundancy and data dependence.
Sample code showing an example of how you can test your code are provided under the files directory in the archive that contains this file.
You should provide appropriate comments to make your source code readable. If your code does not work and there are no comments, you may lose all marks.
Coding Style
You should follow a consistent coding style when writing your source code. Coding style (aka coding standard) refers to the use of appropriate indentation, proper placement of braces, proper formatting of control constructs, and many others. Following a particular coding style consistently will make your source code more readable.
There are many coding standards available (search "C coding style"), but we suggest you consult the
lightweight Linux kernel coding style (see
coding-style). The relevant sections are Sections 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8. Note that you do not have to follow every recommendation you can find in a coding style document, you just have to apply that style consistently.
Program Design:
A fundamental concept in DBMS is the
table. A table consists of zero or more
records or entries, and each record can have one or more
fields or columns. An example of a table that stores information about music albums is shown below:
| id |
title |
year |
artist |
| 10 |
The Dark Side of the Moon |
1973 |
Pink Floyd |
| 14 |
Back in Black |
1980 |
AC/DC |
| 23 |
Their Greatest Hits |
1976 |
Eagles |
| 37 |
Falling into You |
1996 |
Celine Dion |
| 43 |
Come Away With Me |
2002 |
Norah Jones |
| 55 |
21 |
2011 |
Adele |
This table contains 6 records. Each record has 4 fields, namely,
id,
title,
year, and
artist.
In this assignment, you will focus on implementing a single database table with 4 fields (id, title, year, and artist). To guide you in the implementation, high-level design of the table is shown below:
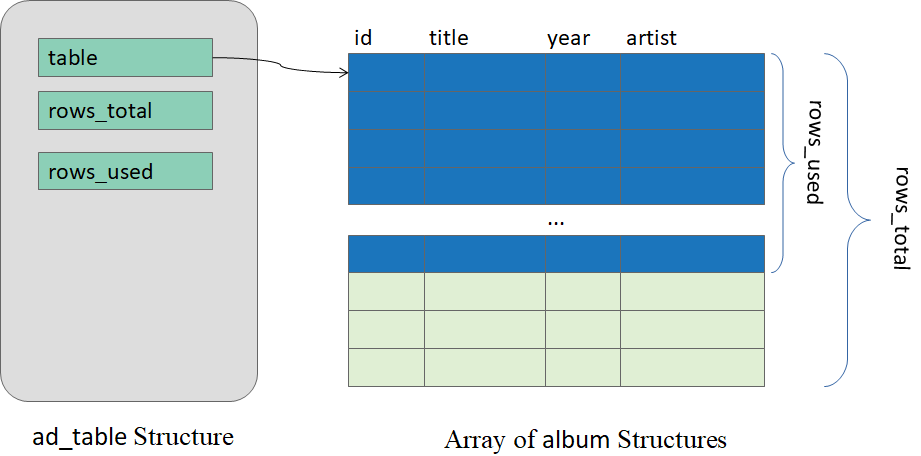
The design consists of a
db_table structure and an array of
album structures that are dynamically allocated. The
db_table structure should have the following member variables:
-
table: a pointer to an array of structures, that is dynamically allocated,
-
rows_total: the total number of rows in the array of structures
-
rows_used: the number of rows in the array of structures that contains valid records.
The array of
album structures will hold the records. This array should be dynamically adjusted using the following scheme:
- Initially, the array should be empty.
rows_total should be set to 0 and rows_used should be set to 0.
- When adding a record and there is unused space in the table (
rows_used is less than rows_total), the record is stored in the next unused row, and rows_used is updated accordingly.
- When adding a record and there is no space in the table (rows_used is equal to
rows_total), additional memory for holding 5 records should be allocated. Then, the record is stored in the next unused row, and rows_used and rows_total are updated accordingly.
- When removing a record, records after the removed record should be moved up by one row so that there will be no gaps in between
used rows. When the number of unused rows reaches 5, the unused rows should be released, and rows_used and rows_total are updated accordingly.
The definition of the
db_table and
album structures are given in the header file named
dbms.h which is provided under the
zip file directory.
Core [45 Marks]
Provide an implementation of a function called
db_show_row for displaying the information stored in a row. The display output should be formatted as follows:
id: title: artist:year
where
id,
title,
artist, and
year should occupy 6, 20, 20, and 4 spaces, respectively. Shorter values should be padded with space, whereas longer values should be truncated to fit within the space. As an example, for the record with id
10, title
"The Dark Side of the Moon", year
1973, and artist
"Pink Floyd", the output should be
⍽⍽⍽⍽10:The Dark Side of the:⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽⍽Pink Floyd:1973
where ⍽ represents a single space. There should be a newline at the end of the line.
The function prototype is given in the header file named
dbms.h which is provided under the
files directory
The function accepts two input parameters:
- Pointer to a
db_table structure (see definition in dbms.h)
- Unsigned integer indicating the row number of the record to be displayed.
If the record exists, the function should return
1, otherwise, it should return
0.
Save the function implementation in a C source file named
dbms.c
You can test your function implementation by compiling
dbms.c together with the file named
t1test.c which is provided under the
zip file directory. Read the contents of
t1test.c to know how to compile and run the resulting executable file.
Completion [15 Marks]
Provide an implementation of a function called
db_add_row for adding a record into the database table. The function prototype is given in the header file named
dbms.h which is provided under the
files directory.
The function accepts two input parameters:
- Pointer to a
db_table structure (see definition in dbms.h)
- Pointer to
album structure (see definition in dbms.h) as input parameter containing the record details to be stored in the table.
As mentioned in the
Program Design section:
- When adding a record and there is unused space in the table (
rows_used is less than rows_total), the record is stored in the next unused row, and rows_used is updated accordingly.
- When adding a record and there is no space in the table (
rows_used is equal to rows_total), additional memory for holding 5 records should be allocated. Then, the record is stored in the next unused row, and rows_used and rows_total are updated accordingly.
The function should always return
1 unless the allocation of additional memory (when needed) fails where it should return
0.
Save the function implementation in a C source file named
dbms.c.
You can test your function implementation by compiling
dbms.c together with the file named t2test.c which is provided under the
zip file directory. Read the contents of
t2test.c to know how to compile and run the resulting executable file.
Challenge[10 Marks]
Provide an implementation of a function called
db_remove_row for removing a record from the database table. The function prototype is given in the header file named
dbms.h which is provided under the
zip file directory.
The function accepts two input parameters:
- Pointer to a
db_table structure (see definition in dbms.h)
- Unsigned long integer specifying the id of the record to be removed.
As mentioned in the
Program Design section:
- When removing a record, records after the removed record should be moved up by one row so that there will be no gaps in between used rows. When the number of unused rows reaches 5, the unused rows should be released, and
rows_used and rows_total are updated accordingly.
The function should return
1 if the removal was successful, otherwise, it should return
0.
Save the function implementation in a C source file named
dbms.c.
You can test your function implementation by compiling
dbms.c together with the file named
t3test.c which is provided under the
files directory. Read the contents of
t3test.c to know how to compile and run the resulting executable file.
Marking Criteria:
| Criteria |
Weight |
Expectations for Full Marks |
| Compilation |
5% |
Compiles without warnings |
| Comments |
10% |
Sufficient and appropriate comments |
| Code Quality |
15% |
Consistent coding style |
| Correctness |
70% |
Handles all test cases correctly (see marks distribution below) |
| Total |
100% |
|
For the
Correctness criteria, the following table shows the marks distribution over the different task types:
 The design consists of a
The design consists of a 